Building a Smarter ETF Portfolio Using Modern Portfolio Theory
How do you decide what ETFs to include in your portfolio and how much to allocate? Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT) offers a clear framework to balance risk and return. Learn how the efficient frontier and tangency portfolio can help you optimize your investments for better results.
When it comes to building an investment portfolio, one question stands out: how do you decide what to include and how much to allocate? Should you go all-in on the S&P 500 (SPY), balance it out with bonds (BND), or sprinkle in some gold (GLD) for safety? These decisions don’t have to be guesswork. Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT) offers a clear, practical framework to balance risk and return.
In this post, we’ll explore how MPT works, introduce terms like the efficient frontier and tangency portfolio, and show how you can use them to refine your investment strategy.
What is Modern Portfolio Theory?
Introduced by economist Harry Markowitz in 1952, Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT) is based on a powerful yet simple idea: combining different types of investments can help you maximize returns while minimizing risk.
Think of your portfolio as a recipe. Some ingredients—like stocks—are spicy and unpredictable, while others—like bonds—are bland but dependable. MPT helps you mix these ingredients in a way that creates a dish that’s both balanced and satisfying. The goal is to find the right proportions to get the best outcome for your risk tolerance.
The Efficient Frontier: Finding the Sweet Spot
The efficient frontier is a visual representation of all the best possible portfolios you can create by combining available ETFs. It’s a curve that shows the portfolios with the best return for a given risk level. That curve also represents the highest Sharpe Ratios for a given combination of ETFs. You remember Sharpe Ratio? We talked about it in our article about The Moving Average Strategy.
Let’s quickly recap: the Sharpe Ratio measures how much return you’re getting for the risk you’re taking. The higher the Sharpe Ratio, the better the portfolio. Portfolios that fall below the efficient frontier aren’t maximizing their potential. Meanwhile, portfolios on the curve are optimal.
A Simple Example: Five ETFs
To illustrate how the efficient frontier works, let’s build a portfolio using five popular ETFs:
• SPY: A broad U.S. stock market ETF (blue).
• QQQ: Focused on technology companies in the Nasdaq (orange).
• BND: A bond ETF for stability (yellow).
• GLD: A gold ETF for diversification (green).
• SMH: A semiconductor ETF for high-growth potential (purple).
Using historical data and simulations (Monte Carlo simulations), we calculate the risk (standard deviation) and expected return for each ETF. The chart below shows these values, with risk on the x-axis and expected return on the y-axis.
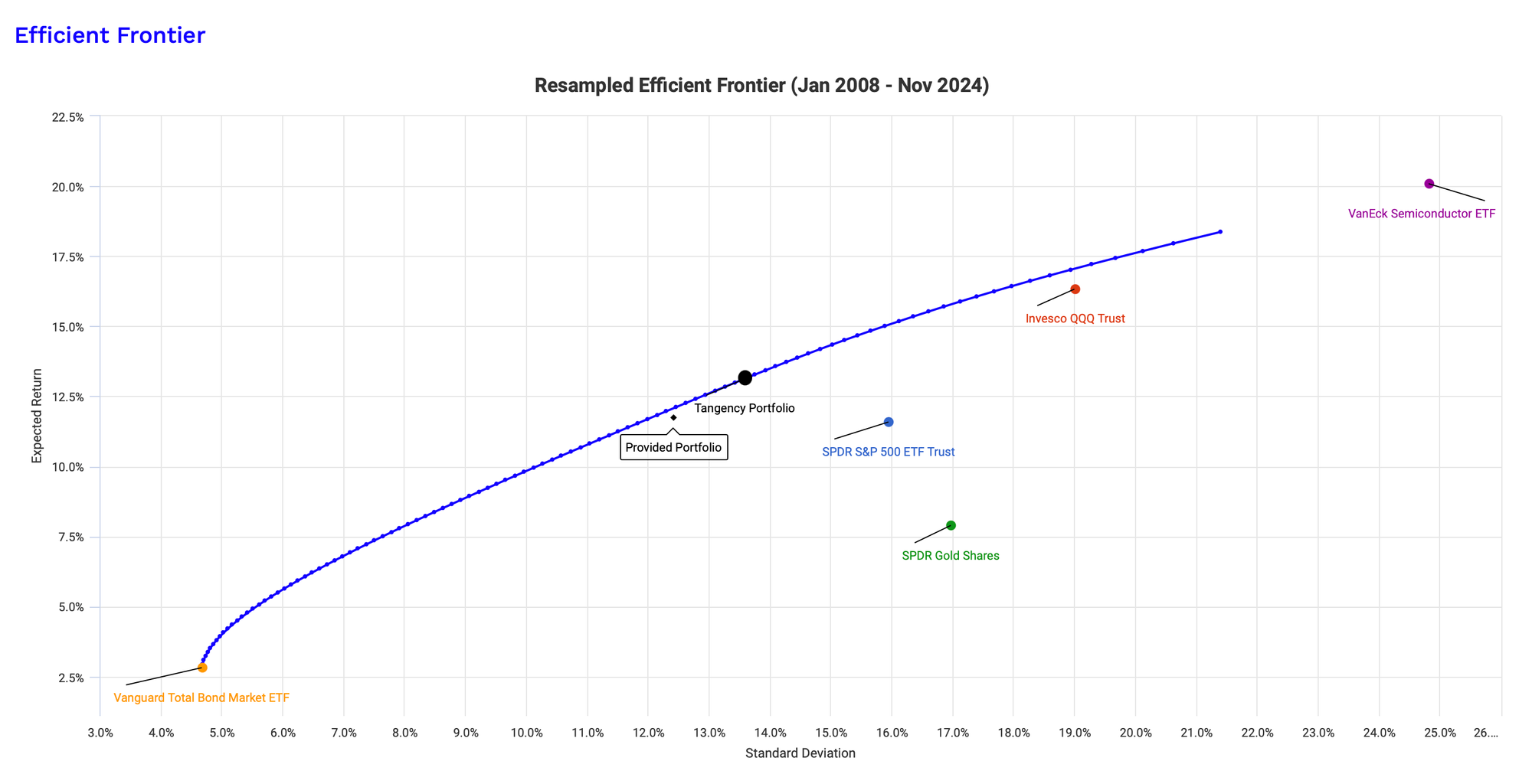
Why Aren’t the ETFs on the Efficient Frontier?
If you look closely, none of the individual ETFs—except for the bond ETF (BND)—sit on the efficient frontier. Why? Because individual assets rarely achieve the ideal balance of risk and return. Instead, a well-crafted combination of assets can achieve better results.
For example:
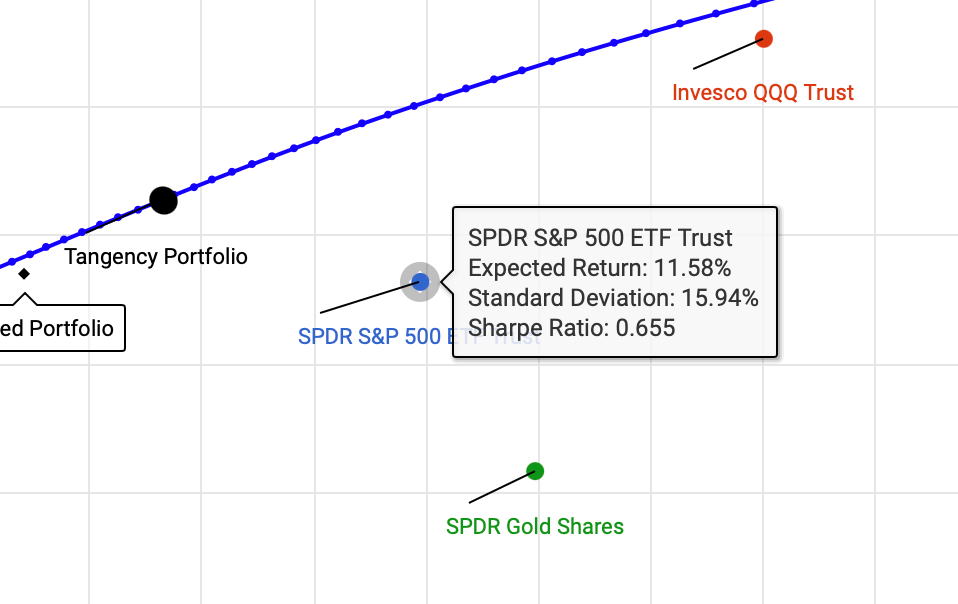
- SPY has an expected return of 11.6% and a risk (standard deviation) of 16%. The Sharpe Ratio is 0.65
- However, a portfolio made up of 3.5% SPY, 33.6% QQQ, 2.8% BND, 24.9% GLD, and 35.2% SMH has the same level of risk (16%) but a higher expected return (15%).
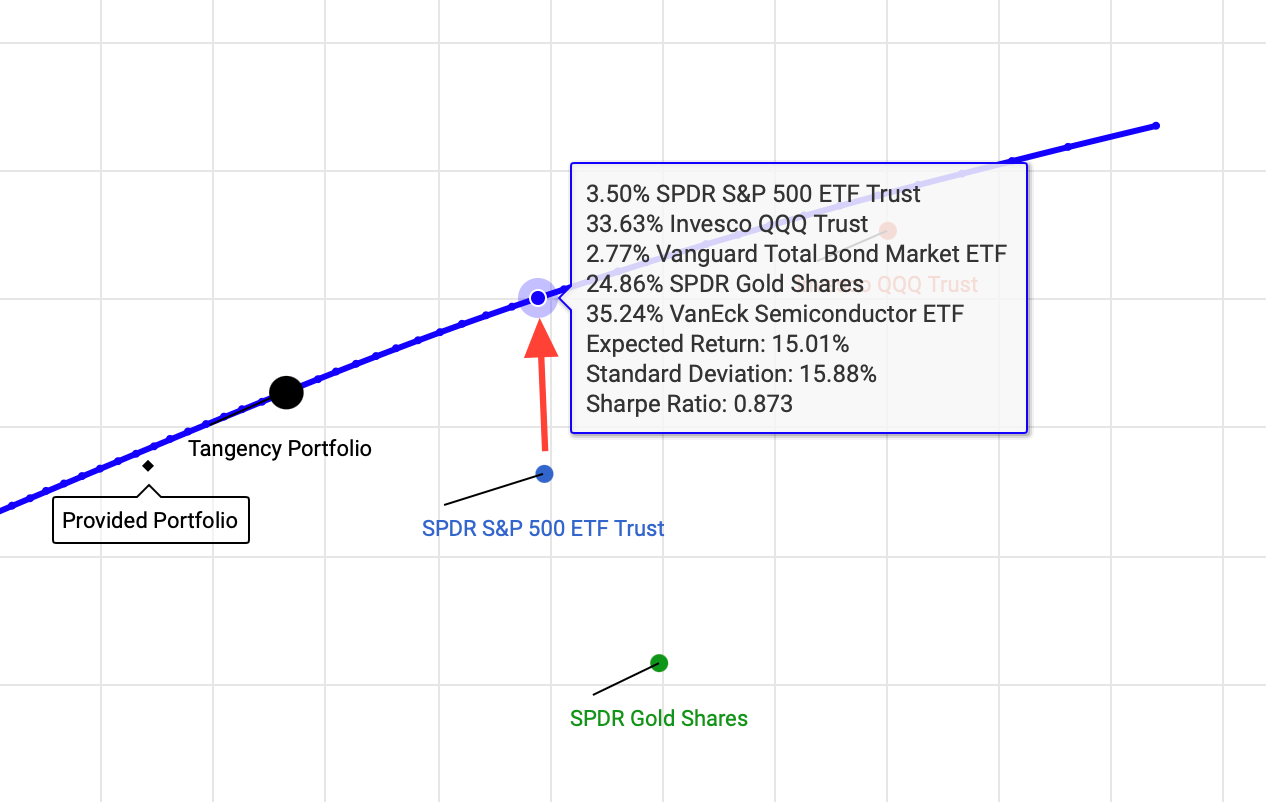
This is the power of diversification and optimization. For the same amount of risk, you get a better return. Why settle for less?
What’s the Big Black Dot? Introducing the Tangency Portfolio
On the efficient frontier, i.e. the representation of all the best possible portfolios, there’s one portfolio that stands out: the tangency portfolio. This portfolio delivers the highest Sharpe Ratio of all portfolios on the efficient frontier, meaning it gives you the best possible return for the risk you’re taking.
Think of it as the “Goldilocks portfolio”—not too risky, not too cautious, but just right. Investors often use the tangency portfolio as the starting point for building a strategy because it’s optimized for risk-adjusted returns.
Comparing Two Portfolios
Let’s compare the tangency portfolio with a simpler approach: an equal-weighted portfolio.
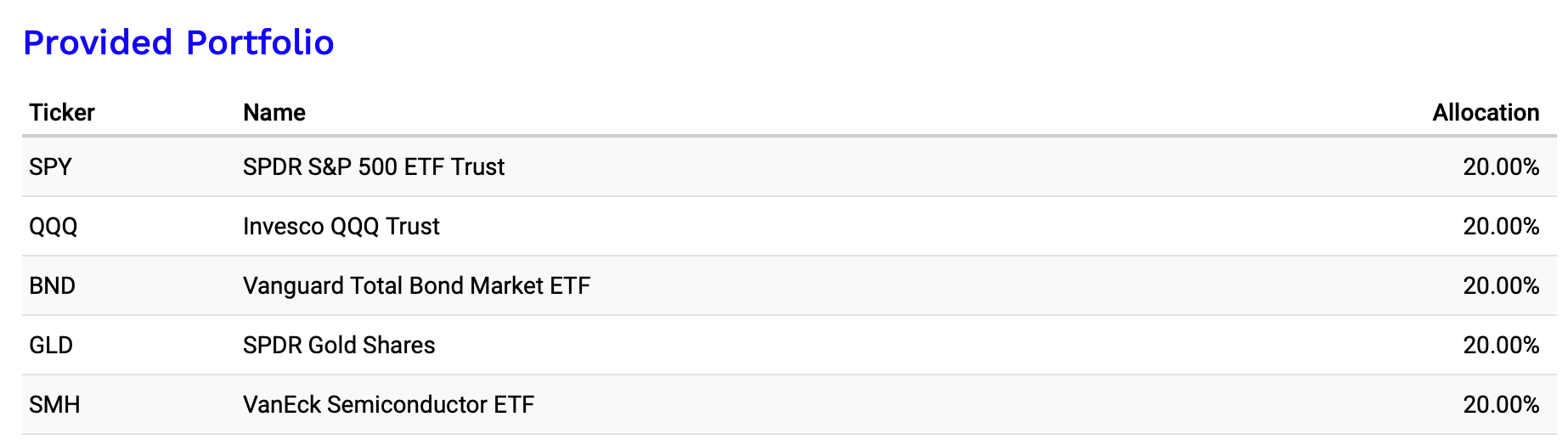
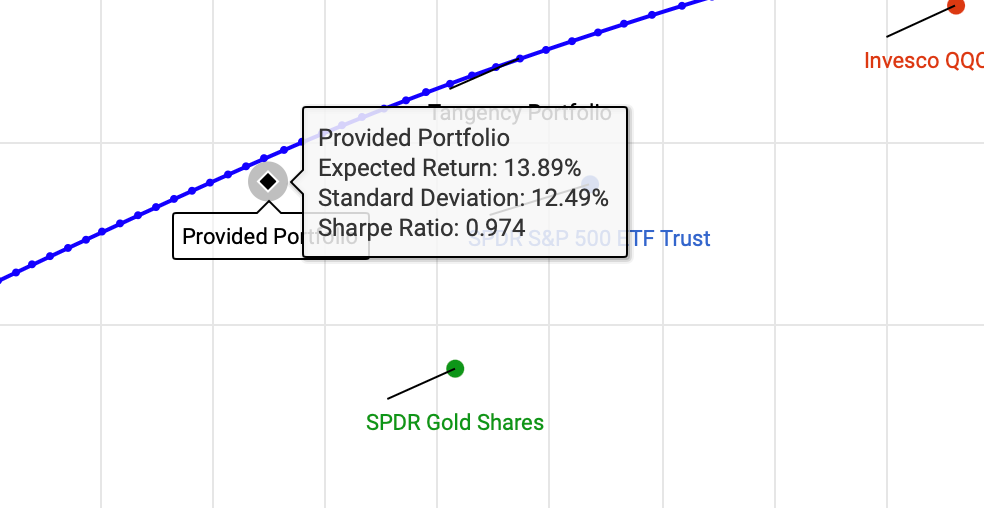
1. The Equal-Weighted Portfolio
This portfolio gives each ETF an equal allocation (20%). It’s easy to set up but doesn’t take into account the unique risk and return characteristics of each asset.
2. The Tangency Portfolio
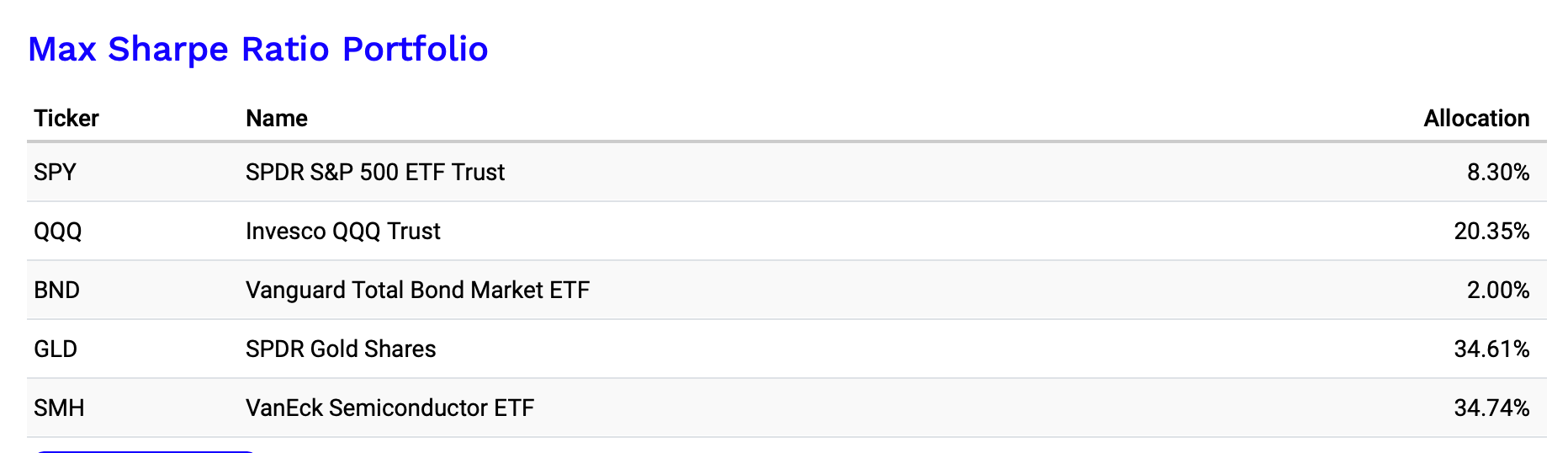
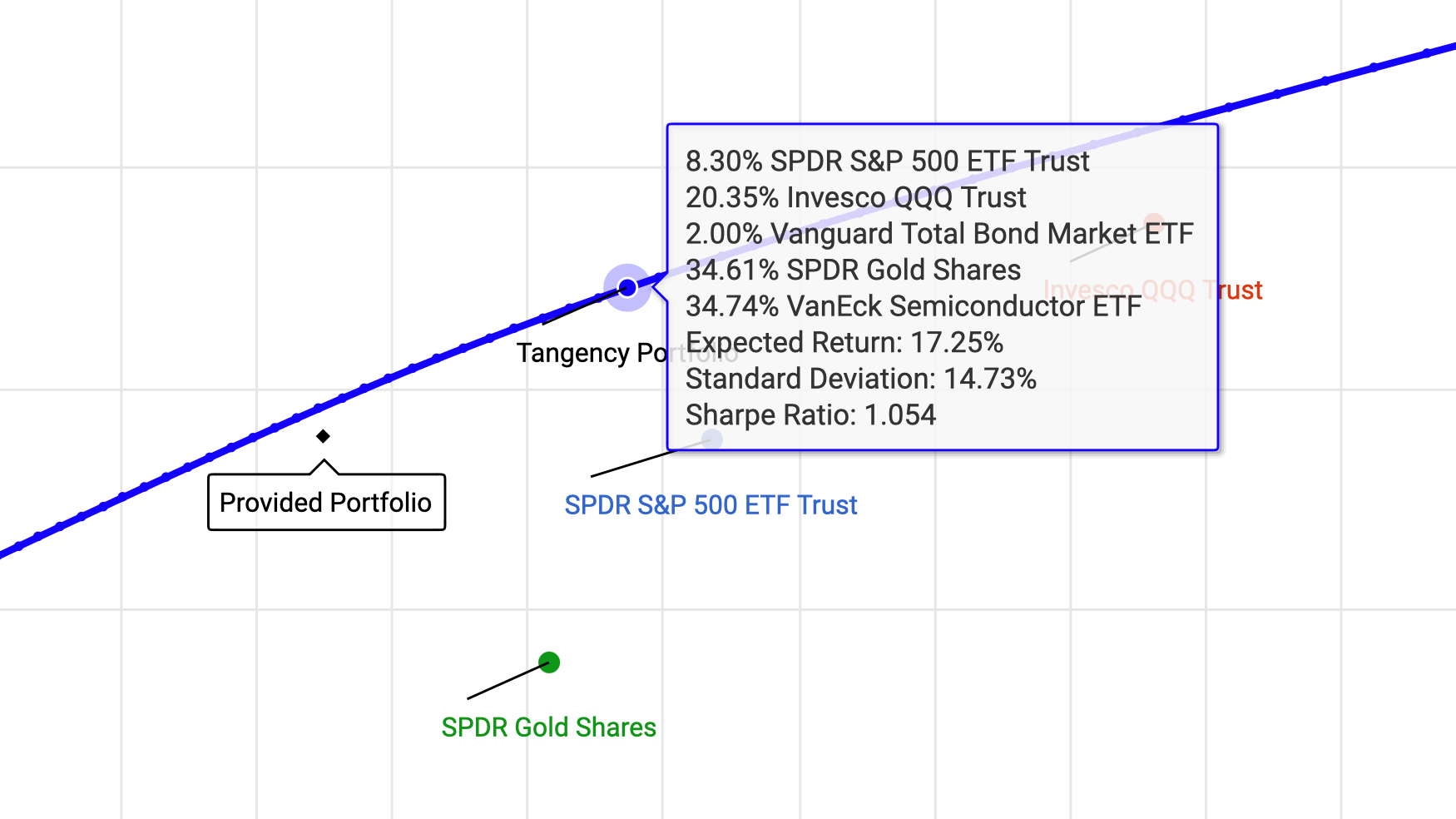
This portfolio is optimized to maximize the Sharpe Ratio. It places significant emphasis on high-growth ETFs like SMH and QQQ, while reducing allocations to more stable assets like BND and balancing the risk with GLD. Here’s the breakdown:
Why the Tangency Portfolio Works
The tangency portfolio excels because it strikes an good balance between risk and return. Here’s how:
Risk-Return Optimization:
By emphasizing high-growth ETFs like SMH and QQQ, which together make up nearly 55% of the portfolio and a significant allocation in GLD, the tangency portfolio captures strong potential returns. At the same time, it minimizes exposure to lower-return assets like BND, which only accounts for 2%.
Diversification:
Including GLD as a significant portion in the portfolio reduces overall volatility because gold often behaves differently from stocks, especially during market turbulence.
Efficient Use of Risk:
The tangency portfolio ensures you’re extracting the maximum possible return for the risk you’re taking—no wasted effort, just optimal performance.
How to Apply This to Your Portfolio
Use Tools to Analyze Your Portfolio:
Platforms like PortfolioVisualizer can help you see where your portfolio stands relative to the efficient frontier.
Start with ETFs:
ETFs like SPY, QQQ, and GLD provide simple, cost-effective access to a wide range of assets.
Focus on Diversification:
Combine assets that behave differently, like stocks and gold, to reduce overall portfolio risk.
Revisit and Adjust:
As markets change, so should your portfolio. Regular rebalancing keeps you aligned with your goals.
Final Thoughts
Modern Portfolio Theory offers a proven way to create better portfolios. By understanding concepts like the efficient frontier and tangency portfolio, you can make more informed decisions about how to allocate your investments.
The best part? You don’t need to guess your way through portfolio building. With tools like PortfolioVisualizer you can create a portfolio that balances risk and reward effectively. If you’re interested in building your own Python notebook to find the tangency portfolio for your ETFs, let us know—we’d love to help you get started.